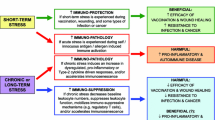
Abstract
A growing number of studies on non-human animals have documented that stressors modulate the expression of yawning. In particular, recent experimental research shows that yawns are initially inhibited following physical stress, but then become potentiated thereafter. However, stress-induced yawning in humans has yet to be demonstrated experimentally. Here, we investigated the temporal relationship between self-reported contagious yawning and an acute physical stressor in 141 human subjects in the laboratory. Using a 2 × 2 between-subjects design, participants either underwent the cold pressor test (CPT) or a matched control condition prior to viewing a contagious yawning stimulus that was either displayed immediately thereafter or following a 20-min delay. Consistent with the comparative literature, we show an interaction between stress and time conditions, whereby both the incidence and frequency of yawning are lowest in the immediate-CPT trials and highest in the delayed-CPT trials. These findings support a homologous effect of acute physical stress on yawning across birds and mammals that may be related to an adaptive thermoregulatory and arousal function.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alomari, R. A., Fernandez, M., Banks, J. B., Acosta, J., & Tartar, J. L. (2015). Acute stress Dysregulates the LPP ERP response to emotional pictures and impairs sustained attention: time-sensitive effects. Brain Sciences, 5(2), 201–219.
Anías-Calderón, J., Verdugo-Díaz, L., & Drucker-Colín, R. (2004). Adrenalectomy and dexamethasone replacement on yawning behavior. Behavioural Brain Research, 154(1), 255–259.
Baenninger, R. (1987). Some comparative aspects of yawning in Betta splendens, Homo sapiens, Panthera leo, and Papio Sphinx. Journal of Comparative Psychology, 101, 349–354.
Baenninger, R. (1997). On yawning and its functions. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 4(2), 198–207.
Baenninger, R., & Greco, M. (1991). Some antecedents and consequences of yawning. Psychological Record, 41(4), 453–460.
Baker, K. C., & Aureli, F. (1997). Behavioural indicators of anxiety: an empirical test in chimpanzees. Behaviour, 134(13), 1031–1050.
Banks, J. B., Tartar, J. L., & Welhaf, M. S. (2014). Where's the impairment: an examination of factors that impact sustained attention following a stressor. Cognition & Emotion, 28(5), 856–866.
Barbizet, J. (1958). Yawning. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 21(3), 203–209.
Bartholomew, A. J., & Cirulli, E. T. (2014). Individual variation in contagious yawning susceptibility is highly stable and largely unexplained by empathy or other known factors. PloS One, 9(3), e91773.
Beerda, B., Schilder, M. B., van Hooff, J. A., de Vries, H. W., & Mol, J. A. (1998). Behavioural, saliva cortisol and heart rate responses to different types of stimuli in dogs. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 58(3), 365–381.
Brusselmans, G., Caralho, H. N., De Schamphelaere, E., Devulder, J., & Crombez, G. (2015). Skin temperature during cold pressor test in fibromyalgia: an evaluation of the autonomic nervous system? Acta Anaesthesiologica Belgica, 66(1), 19–27.
Carrillo, M., Migliorati, F., Bruls, R., Han, Y., Heinemans, M., Pruis, I., et al. (2015). Repeated witnessing of conspecifics in pain: effects on emotional contagion. PloS One, 10(9), e0136979.
Castles, D. L., Whiten, A., & Aureli, F. (1999). Social anxiety, relationships and self-directed behaviour among wild female olive baboons. Animal Behaviour, 58(6), 1207–1215.
Chrousos, G. P. (1998). Stressors, stress, and neuroendocrine integration of the adaptive response: the 1997 Hans Selye memorial lecture. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 851(1), 311–335.
Chwałczyńska, A., Gruszka, K., Całkosiński, I., & Sobiech, K. A. (2015). Thermovision analysis changes of human hand surface temperature in cold pressor test. BioMed Research International, 2015. doi:10.1155/2015/783642.
Cornelisse, S., van Stegeren, A. H., & Joëls, M. (2011). Implications of psychosocial stress on memory formation in a typical male versus female student sample. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 36(4), 569–578.
Daquin, G., Micallef, J., & Blin, O. (2001). Yawning. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 5(4), 299–312.
Darwin, C. R. (1872). The expression of the emotions in man and animals. London: John Murray.
Demuru, E., & Palagi, E. (2012). In bonobos yawn contagion is higher among kin and friends. PLoS One, 7(11), e49613.
Deputte, B. L. (1994). Ethological study of yawning in primates. I. Quantitative analysis and study of causation in two species of old world monkeys (Cercocebus Albigena and Macaca fascicularis). Ethology, 98, 221–245.
Dreschel, N. A., & Granger, D. A. (2005). Physiological and behavioral reactivity to stress in thunderstorm-phobic dogs and their caregivers. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 95(3), 153–168.
Edelson, J. T., & Robertson, G. L. (1986). The effect of the cold pressor test on vasopressin secretion in man. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 11(3), 307–316.
Eldakar, O. T., Dauzonne, M., Prilutzkaya, Y., Garcia, D., Thadal, C., & Gallup, A. C. (2015). Temperature-dependent variation in self-reported contagious yawning. Adaptive Human Behavior and Physiology, 1(4), 460–466.
Fenner, K., Yoon, S., White, P., Starling, M., & McGreevy, P. (2016). The effect of noseband tightening on horses’ behavior, eye temperature, and cardiac responses. PloS One, 11(5), e0154179.
Frank, S. M., & Raja, S. N. (1994). Reflex cutaneous vasoconstriction during cold pressor test is mediated through α-adrenoceptors. Clinical Autonomic Research, 4(5), 257–261.
Gallup, A. C. (2011). Why do we yawn? Primitive versus derived features. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 35(3), 765–769.
Gallup, A. C. (2016). Ambient temperature modulates yawning. Temperature, 3(1), 23–24.
Gallup, A. C., & Church, A. M. (2015). The effects of intranasal oxytocin on contagious yawning. Neuroscience Letters, 607, 13–16.
Gallup, A. C., & Clark, A. B. (2015). Commentary: yawning, acute stressors, and arousal reduction in Nazca booby adults and nestlings. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 1654.
Gallup, A. C., & Eldakar, O. T. (2011). Contagious yawning and seasonal climate variation. Frontiers in Evolutionary Neuroscience, 3, 1–4.
Gallup, A. C., & Eldakar, O. T. (2013). The thermoregulatory theory of yawning: what we know from over 5 years of research. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 6, 1–13.
Gallup, A. C., & Gallup Jr., G. G. (2007). Yawning as a brain cooling mechanism: nasal breathing and forehead cooling diminish the incidence of contagious yawning. Evolutionary Psychology, 5, 92–101.
Gallup, A. C., & Gallup Jr., G. G. (2008). Yawning and thermoregulation. Physiology & Behavior, 95(1), 10–16.
Gallup Jr., G. G., & Gallup, A. C. (2010). Excessive yawning and thermoregulation: two case histories of chronic, debilitating bouts of yawning. Sleep and Breathing, 14(2), 157–159.
Gallup, A. C., & Gallup, J. A. (2013). Frequent yawning as an initial signal of fever relief. Medical Hypotheses, 81(6), 1034–1035.
Gallup, A. C., & Massen, J. J. (2016). There is no difference in contagious yawning between men and women. Royal Society Open Science, 3(9), 160174.
Gallup, A. C., Miller, M. L., & Clark, A. B. (2009). Yawning and thermoregulation in budgerigars, Melopsittacus undulatus. Animal Behaviour, 77(1), 109–113.
Gallup, A. C., Miller, M. L., & Clark, A. B. (2010). The direction and range of ambient temperature change influences yawning in budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulatus). Journal of Comparative Psychology, 124(2), 133.
Gallup, A. C., Miller, R. R., & Clark, A. B. (2011). Changes in ambient temperature trigger yawning but not stretching in rats. Ethology, 117(2), 145–153.
Gallup, A., Church, A. M., Miller, H., Risko, E. F., & Kingstone, A. (2016a). Social presence diminishes contagious yawning in the laboratory. Scientific Reports, 6, 25045.
Gallup, A. C., Church, A. M., & Pelegrino, A. J. (2016b). Yawn duration predicts brain weight and cortical neuron number in mammals. Biology Letters, 12(10), 20160545.
Goodall, J. (1968). A preliminary report on expressive movements and communication in the Gombe stream chimpanzees. In P. C. Jay (Ed.), Primates: studies in adaptation and variability. New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
Górecka-Bruzda, A., Fureix, C., Ouvrard, A., Bourjade, M., & Hausberger, M. (2016). Investigating determinants of yawning in the domestic (Equus caballus) and Przewalski (Equus ferus przewalskii) horses. The Science of Nature, 103(9–10), 72.
Greco, M., & Baenninger, R. (1989). Self-report as a valid measure of yawning in the laboratory. Bulletin of the Psychonomic Society, 27(1), 75–76.
Greco, M., Baenninger, R., & Govern, J. (1993). On the context of yawning: when, where, & why? The Psychological Record, 43(2), 175.
Guggisberg, A. G., Mathis, J., Schnider, A., & Hess, C. W. (2010). Why do we yawn? Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 34(8), 1267–1276.
Hadidian, J. (1980). Yawning in an old world monkey, Macaca nigra (primates: Cercopithecidae). Behaviour, 75(3), 133–147.
Hennessy, M. B., Williams, M. T., Miller, D. D., Douglas, C. W., & Voith, V. L. (1998). Influence of male and female petters on plasma cortisol and behaviour: can human interaction reduce the stress of dogs in a public animal shelter? Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 61(1), 63–77.
Itoi, K., & Sugimoto, N. (2010). The brainstem noradrenergic systems in stress, anxiety and depression. Journal of Neuroendocrinology, 22(5), 355–361.
Klopp, C., Garcia, C., Schulman, A. H., Ward, C. P., & Tartar, J. L. (2012). Acute social stress increases biochemical and self report markers of stress without altering spatial learning in humans. Neuroendocrinology Letters, 33(4), 425–430.
Kubota, N., Amemiya, S., Yanagita, S., Nishijima, T., & Kita, I. (2014). Emotional stress evoked by classical fear conditioning induces yawning behavior in rats. Neuroscience Letters, 566, 182–187.
Leone, A., Ferrari, P. F., & Palagi, E. (2014). Different yawns, different functions? Testing social hypotheses on spontaneous yawning in Theropithecus gelada. Scientific Reports, 4, 4010.
Liang, A. C., Grace, J. K., Tompkins, E. M., & Anderson, D. J. (2015). Yawning, acute stressors, and arousal reduction in Nazca booby adults and nestlings. Physiology & Behavior, 140, 38–43.
Maestripieri, D., Schino, G., Aureli, F., & Troisi, A. (1992). A modest proposal: displacement activities as an indicator of emotions in primates. Animal Behaviour, 44(5), 967–979.
Mariti, C., Gazzano, A., Moore, J. L., Baragli, P., Chelli, L., & Sighieri, C. (2012). Perception of dogs’ stress by their owners. Journal of Veterinary Behavior: Clinical Applications and Research, 7(4), 213–219.
Massen, J. J., Dusch, K., Eldakar, O. T., & Gallup, A. C. (2014). A thermal window for yawning in humans: yawning as a brain cooling mechanism. Physiology & Behavior, 130, 145–148.
Massen, J. J., Church, A. M., & Gallup, A. C. (2015). Auditory contagious yawning in humans: an investigation into affiliation and status effects. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 1735.
Miller, M. L., Gallup, A. C., Vogel, A. R., & Clark, A. B. (2010). Handling-stress initially inhibits, but then potentiates yawning in budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulatus). Animal Behaviour, 80, 615–619.
Miller, M. L., Gallup, A. C., Vogel, A. R., & Clark, A. B. (2012). Auditory disturbances promote temporal clustering of yawning and stretching in small groups of budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulatus). Journal of Comparative Psychology, 126(3), 324.
Mizeva, I., Frick, P., & Podtaev, S. (2015). Skin blood flow and temperature oscillations during cold pressor test. In Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE (pp. 7382–7385). IEEE.
Moyaho, A., & Valencia, J. (2002). Grooming and yawning trace adjustment to unfamiliar environments in laboratory Sprague-Dawley rats (Rattus norvegicus). Journal of Comparative Psychology, 116(3), 263.
Norscia, I., Demuru, E., & Palagi, E. (2016). She more than he: gender bias supports the empathic nature of yawn contagion in Homo sapiens. Royal Society open science, 3(2), 150459.
Oka, T., Oka, K., & Hori, T. (2001). Mechanisms and mediators of psychological stress-induced rise in core temperature. Psychosomatic Medicine, 63(3), 476–486.
Olivier, B., Zethof, T., Pattij, T., van Boogaert, M., van Oorschot, R., Leahy, C., et al. (2003). Stress-induced hyperthermia and anxiety: pharmacological validation. European Journal of Pharmacology, 463(1), 117–132.
Part, C. E., Kiddie, J. L., Hayes, W. A., Mills, D. S., Neville, R. F., Morton, D. B., & Collins, L. M. (2014). Physiological, physical and behavioural changes in dogs (Canis familiaris) when kennelled: testing the validity of stress parameters. Physiology & Behavior, 133, 260–271.
Platek, S. M., Critton, S. R., Myers, T. E., & Gallup, G. G. (2003). Contagious yawning: the role of self-awareness and mental state attribution. Cognitive Brain Research, 17(2), 223–227.
Provine, R. R. (1986). Yawning as a stereotyped action pattern and releasing stimulus. Ethology, 72(2), 109–122.
Provine, R. R. (2005). Yawning: the yawn is primal, unstoppable and contagious, revealing the evolutionary and neural basis of empathy and unconscious behavior. American Scientist, 93(6), 532–539.
Redican, W. K. (1982). An evolutionary perspective on human facial displays. In P. Ekman (Ed.), Emotion in the human face (2nd ed., pp. 212–280). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Schilder, M. B., & van der Borg, J. A. (2004). Training dogs with help of the shock collar: short and long term behavioural effects. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 85(3), 319–334.
Schino, G., & Aureli, F. (1989). Do men yawn more than women? Ethology and Sociobiology, 10(5), 375–378.
Schwabe, L., Haddad, L., & Schachinger, H. (2008). HPA axis activation by a socially evaluated cold-pressor test. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 33(6), 890–895.
Shoup-Knox, M. L., Gallup, A. C., Gallup Jr., G. G., & McNay, E. C. (2010). Yawning and stretching predict brain temperature changes in rats: support for the thermoregulatory hypothesis. Frontiers in Evolutionary Neuroscience, 2, 1–5.
Smith, E. O. (1999) Yawning: an evolutionary perspective. Human Evolution, 14(3), 191–198.
Spencer, R. L., & Deak, T. (2016). A users guide to HPA axis research. Physiology & Behavior. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.11.014.
Thompson, S. B. (2011). Born to yawn? Cortisol linked to yawning: a new hypothesis. Medical Hypotheses, 77(5), 861–862.
Thompson, S. B., & Bishop, P. (2012). Born to yawn? Understanding yawning as a warning of the rise in cortisol levels: randomized trial. Interactive Journal of Medical Research, 1(2), e4.
Thompson, S. B., Frankham, C., & Bishop, P. (2014a). The art of capturing a yawn using the science of nerve impulses and cortisol levels in a randomized controlled trial. Thompson Cortisol Hypothesis as a potential predictor of neurological impairment. International Journal of Arts & Sciences, 7(3), 529.
Thompson, S. B., Rose, K., & Richer, S. (2014b). Yawning with cortisol: examining the neuroscience behind the Thompson cortisol hypothesis for supporting rehabilitation of neurologically impaired individuals. Journal of Neuroscience & Rehabilitation, 1(1), 1–11.
Troisi, A., Aureli, F., Schino, G., Rinaldi, F., & Angelis, N. (1990). The influence of age, sex, and rank on yawning behavior in two species of macaques (Macaca fascicularis and M. fuscata). Ethology, 86(4), 303–310.
Tsigos, C., & Chrousos, G. P. (2002). Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, neuroendocrine factors and stress. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 53(4), 865–871.
Tufik, S., de Luca Nathan, C., Neumann, B., Hipólide, D. C., Lobo, L. L., de Medeiros, R., et al. (1995). Effects of stress on drug-induced yawning: constant vs. intermittent stress. Physiology & Behavior, 58(1), 181–184.
Van der Heyden, J. A., Zethof, T. J., & Olivier, B. (1997). Stress-induced hyperthermia in singly housed mice. Physiology & Behavior, 62(3), 463–470.
Vick, S. J., & Paukner, A. (2010). Variation and context of yawns in captive chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes). American Journal of Primatology, 72(3), 262–269.
Viena, T. D., Banks, J. B., Barbu, I. M., Schulman, A. H., & Tartar, J. L. (2012). Differential effects of mild chronic stress on cortisol and S-IgA responses to an acute stressor. Biological Psychology, 91(2), 307–311.
von Baeyer, C. L., Piira, T., Chambers, C. T., Trapanotto, M., & Zeltzer, L. K. (2005). Guidelines for the cold pressor task as an experimental pain stimulus for use with children. The Journal of Pain, 6(4), 218–227.
Walløe, L. (2016). Arterio-venous anastomoses in the human skin and their role in temperature control. Temperature, 3(1), 92–103.
Walusinski, O. (2006). Yawning: unsuspected avenue for a better understanding of arousal and interoception. Medical Hypotheses, 67(1), 6–14.
Walusinski, O. (2009). Yawning in diseases. European Neurology, 62(3), 180–187.
Walusinski, O. (2014). How yawning switches the default-mode network to the attentional network by activating the cerebrospinal fluid flow. Clinical Anatomy, 27(2), 201–209.
Washington, L. L., Gibson, S. J., & Helme, R. D. (2000). Age-related differences in the endogenous analgesic response to repeated cold water immersion in human volunteers. Pain, 89(1), 89–96.
Watson, J. D., & Nance, P. W. (1994). Vascular effects of a modified cold pressor test in spinal cord injured and able-bodied men. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 75(1), 59–62.
Zannella, A., Norscia, I., Stanyon, R., & Palagi, E. (2015). Testing yawning hypotheses in wild populations of two strepsirrhine species: Propithecus verreauxi and Lemur catta. American Journal of Primatology, 77(11), 1207–1215.
Zethof, T. J., Van Der Heyden, J. A., Tolboom, J. T., & Olivier, B. (1994). Stress-induced hyperthermia in mice: a methodological study. Physiology & Behavior, 55(1), 109–115.
Zethof, T. J., Van Der Heyden, J. A., Tolboom, J. T., & Olivier, B. (1995). Stress-induced hyperthermia as a putative anxiety model. European Journal of Pharmacology, 294(1), 125–135.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 31 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eldakar, O.T., Tartar, J.L., Garcia, D. et al. Acute Physical Stress Modulates the Temporal Expression of Self-Reported Contagious Yawning in Humans. Adaptive Human Behavior and Physiology 3, 156–170 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40750-017-0060-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40750-017-0060-5